Description
Antifungal agents are medications used to treat fungal infections. Based on their chemical structure and mechanism of action, they are categorized into several classes:
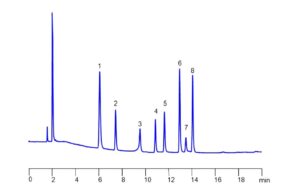
Fluconazole: A triazole antifungal used to treat and prevent superficial and systemic fungal infections.
Ketoconazole: An imidazole antifungal, often used topically due to potential side effects with oral use.
Climbazole: An imidazole used in hair care products to manage dandruff.
Clotrimazole: Treats infections such as vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and ringworm.
Itraconazole: A triazole effective for a wide range of systemic fungal infections.
Terbinafine: An allylamine antifungal targeting skin and nail infections like athlete’s foot.
Econazole: An imidazole used for skin infections such as athlete’s foot and ringworm.
Miconazole: A broad-spectrum imidazole used for skin and vaginal fungal infections.
Triclosan: A broad-spectrum antimicrobial with some antifungal activity; its use has been restricted in many regions due to safety concerns.
Most azole antifungals—such as fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, climbazole, clotrimazole, econazole, and miconazole—act by inhibiting lanosterol 14α-demethylase, an enzyme essential for ergosterol synthesis in fungal cell membranes. Terbinafine inhibits squalene epoxidase, while triclosan targets fatty acid synthesis.
Analytical Method:
These antifungal agents can be separated, retained, and analyzed on a Zodiac HST B mixed-mode stationary phase column. The method employs a gradient elution using a mobile phase of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and sulfuric acid as a buffer. Detection is performed using UV at 200 nm.
Condition
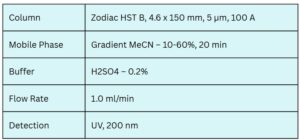
Column Name : Zodiac HST B
Compound Name :
Get Your Quote or Call: 040-29881474
We focus on supporting laboratory workflows & optimizing lab-wide operations
