Description
Acetylcholine and choline are structurally related compounds that serve distinct but interconnected roles, particularly within the nervous system.
Choline
Definition: Choline is an essential nutrient classified within the B-vitamin complex.
Chemical Structure: It is a quaternary ammonium salt, commonly represented as (N(CH₃)₃⁺), featuring a positively charged nitrogen atom.
Function: Choline is a precursor for several biologically important molecules, including phospholipids (critical for cell membrane structure) and the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. It also supports liver function and cellular membrane integrity.
Dietary Sources: Rich dietary sources include eggs, meat, fish, nuts, and various vegetables. It is also available as a dietary supplement.
Acetylcholine
Definition: Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that facilitates communication between neurons and between neurons and muscles.
Chemical Structure: It is synthesized from choline and acetyl coenzyme A, with the molecular structure (CH₃COOCH₂CH₂N(CH₃)₃⁺).
Function: Acetylcholine is essential for signal transmission across synapses, playing a vital role in muscle contraction, autonomic nervous system regulation, and cognitive functions like memory and learning.
Synthesis and Release: It is produced in nerve terminals and released into the synaptic cleft upon nerve stimulation. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase rapidly degrades it to terminate its action.
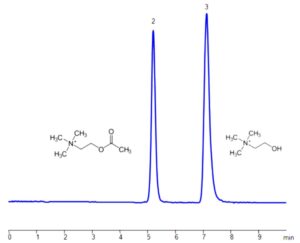
Analytical Method
Acetylcholine and choline can be effectively retained, separated, and analyzed using a Zodiac HST TH mixed-mode stationary phase column. The analysis is carried out using an isocratic method with a straightforward mobile phase consisting of water, acetonitrile (MeCN), and ammonium acetate as the buffer. Detection is performed using evaporative light scattering detection (ELSD).
Condition
Get Your Quote or Call: 040-29881474
We focus on supporting laboratory workflows & optimizing lab-wide operations
